urine test for intestinal permeability|what causes increased intestinal permeability : specialty store The lactulose/mannitol test measures levels of both sugars in a patient’s urine after oral ingestion. Lactulose and mannitol are both oligosaccharides. Their differing molecular weights . Resultado da Mídias de comparação é o sistema que o Fatal Model usa visando gerar mais credibilidade aos perfis.. Todas as mídias de comparação são analisadas por nossa equipe. Lembre-se: sempre que ficar com dúvida se as mídias de algum acompanhante são verdadeiras, venha aqui e de uma espiada para .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBDespués de un reencuentro con su pasado, Tamara — una ex-ortodoxa judia convertida a una femenista rockera — se separa de su novio, rebelandose contra el amor romántico y la monogamia para emprender un camino de exploración en busca de su propio deseo. Comedia 2022. Lali Espósito, Verónica Llinás, Vera Spinetta. Títulos relacionados.
Leaky Gut 101 |. Before You Test |. Stool Tests |. Zonulin Tests |. Antibody Tests |. Lactulose:Mannitol Tests |. Clinical Perspective |. Leaky Gut Treatments. If you’re concerned .
The lactulose/mannitol test measures levels of both sugars in a patient’s urine after oral ingestion. Lactulose and mannitol are both oligosaccharides. Their differing molecular weights . (1) Lactulose / Mannitol Testing (urine) This lab test has been used for over 40 years, and measures the ability of two sugar molecules, lactulose and mannitol, to permeate through the intestinal epithelial barrier .
Intestinal permeability was measured using the lactulose and mannitol excretion test in all healthy controls. The results were expressed as the ratio of excretion of the ingested dose of . The Intestinal Permeability Assessment directly measures the ability of two non-metabolized sugar molecules to permeate the intestinal mucosa. It assesses small intestinal absorption and barrier function in the .
The lactulose-mannitol (L:M) test is another widely used test to assess gut barrier function. It measures the levels of the sugar molecules lactulose and mannitol in the urine. Lactulose isn’t normally absorbed in the . As well as a blood test, you can test for leaky gut through looking at zonulin in a stool sample (which is included in our Ultimate Gut Health Test). You can also take a urine . This study provides information on the optimal time to collect urine in the USE test for assessing small intestinal and colonic permeability. It also provides more convincing .Intestinal permeability is most commonly measured indirectly in humans by the fractional urinary excretion of orally ingested probes that cross the intestinal epithelium by the paracellular pathway, enter the bloodstream, are filtered by .
Our laboratory uses stool, breath, and urine specimens to uncover information about gut inflammation, immune function, digestion, absorption, the microbiome, infections, and gut mucosal integrity. . Intestinal Permeability Assessment .
Intestinal permeability was measured using the urinary lactulose and mannitol excretion test in all subjects. The primary endpoints for the study were the cumulative excretion of liquid and encapsulated lactulose and mannitol during three nonoverlapping intervals: 0–2, 2–8, and 8–24 h, and in addition the 0–8-h cumulative excretion of . Test Code 2011 | Changes in intestinal permeability are associated with many health conditions including autism, autoimmune disorders, food sensitivities and inflammatory bowel disease. This ‘leaky gut’ causes disease because the perturbed intestinal barrier allows toxic molecules to enter the bloodstream and poison the body. Intestinal permeability can be .The Leaky Gut Test (or Intestinal Permeability Test) is a noninvasive gastrointestinal test that measures small intestinal absorption and barrier function in the bowel. Malabsorption and increased intestinal permeability (leaky gut) can be .
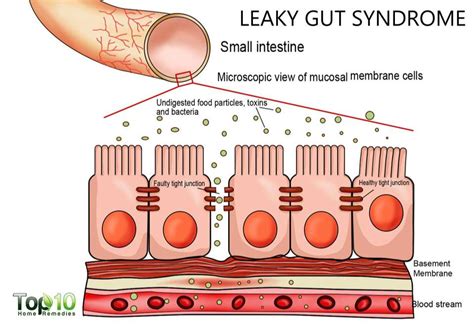
Definition of intestinal permeability Definition of intestinal permeability and intestinal barrier. The term "mucosal barrier" was adopted by Cummings in 2004 to describe the complex structure that separates the internal milieu from the luminal environment [].The physical barrier includes a cellular component consisting of the vascular endothelium, the epithelial cell .
This test utilizes urine specimens for measuring intestinal permeability. Intestinal permeability is a very important factor in determining overall health. The intestinal mucosa, or lining, is a one-cell layer thick barrier between the contents of the intestines and the body’s tissues. The interior Here, we describe an ex vivo intestinal permeability assay, X-IPA, for quantitative analysis of gut permeability dynamics at the whole-tissue level. . Statistical significance between two groups . Intestinal permeability is an important diagnostic marker, yet its determination by established tests, which measure the urinary excretion of orally administered tracer molecules, is time consuming and can only be performed prospectively. Here, we aim to validate proposed surrogate biomarkers, which allow measuring intestinal permeability more easily. In this . Intestinal permeability is an important diagnostic marker, yet its determination by established tests, which measure the urinary excretion of orally administered tracer molecules, is time consuming and can only be performed prospectively. Here, we aim to validate proposed surrogate biomarkers, which allow measuring intestinal permeability more .
Intestinal Permeability Tests. Urine Lactulose Mannitol Test: The use of sugar molecules was one of the first non-invasive laboratory techniques for assessing intestinal permeability. The lactulose-mannitol, or differential sugar test, requires administering an equal, simultaneous oral dose of both a disaccharide (lactulose), . Urinary excretion of two orally-administered non-metabolizable sugars, lactulose and mannitol, is a valuable marker for evaluating intestinal permeability. Usually this test involves a time consuming procedure of about 5 hour's urine collection, which makes the test incompatible to some extent. As t . Leaky gut syndrome is a collection of symptoms attributed to the idea that the intestinal barrier is impaired, allowing toxins from the intestines (the "gut") to enter the bloodstream.
windows hard drive test windows 10
Methods to determine intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation during liver disease . it is easily detected in plasma or urine in the setting of intestinal ischemia (Gollin et . Deutz NE, Brouns F, Brummer RJ. The sensitivity of the lactulose/rhamnose gut permeability test. European journal of clinical investigation. 1999; 29:160 . The sensitivity and reproducibility of the methodology for detecting each sugar in urine samples during the dual sugar absorption test for intestinal permeability was also tested and showed good peak resolution of lactulose and mannitol at 5.9 and 10.4 min, respectively, in all samples collected over a 6 h period of testing. Urinary excretion of two orally-administered non-metabolizable sugars, lactulose and mannitol, is a valuable marker for evaluating intestinal permeability. Usually this test involves a time consuming procedure of about 5 hour’s urine collection, which makes the test incompatible to some extent. As the results are expressed as the ratio of lactulose and . An intestinal permeability assessment can also measure the ability of two sugar molecules to permeate the gut lining — lactulose and mannitol. This leaky gut test checks for levels of the two sugars present in .
The degree of intestinal permeability or malabsorption is reflected in the levels of the two sugars recovered in the urine samples. Array 2 —Intestinal Antigenic Permeability Screen The Intestinal Antigenic Permeability Screen . A combination of the probe molecules lactulose, mannitol and sucralose, also known as the triple sugar test (TST), was selected based on reports of increased excretion in urine after intestinal . Increased zonulin levels correlate with health and disease and are the only recognized biomarker that contributes to intestinal permeability (leaky gut). . involves the oral ingestion of lactulose and mannitol and then measurement of their levels in the urine. This helps to test barrier function. Mannitol is a small sugar molecule that’s .
Background Oral monosaccharides and disaccharides are used to measure in vivo human gut permeability through urinary excretion. Aims 1. To obtain normative data on small intestinal and colonic . Background A widely used method in assessing small bowel permeability is the lactulose:mannitol test, where the lactulose:mannitol ratio (LMR) is measured. However, there is discrepancy in how the test is conducted and in the values of LMR obtained across studies. This meta-analysis aims to determine LMR in healthy subjects, coeliac and Crohn’s disease. . Sugar intestinal permeability assessment has also been conducted through urinary bladder urethral catheterization or cystocentesis in pigs, dogs, and cats. 16–18 For larger animals, bags that attach to animals are also used to collect urine for the sugar test. 19, 20 These approaches are much more technically challenging.
The easiest way to test for leaky gut is through a urine test (more on this below), but there are a few ways you can investigate leaky gut through taking a blood sample. These include: Serum zonulin . Intestinal permeability (more commonly known as leaky gut) is a normal physiological function—but problems arise when your gut is too leaky . The healthy gut restricts macromolecular and bacterial movement across tight junctions, while increased intestinal permeability accompanies many intestinal disorders. Dual sugar absorption tests . Definition of intestinal permeability and intestinal barrier. The term "mucosal barrier" was adopted by Cummings in 2004 to describe the complex structure that separates the internal milieu from the luminal environment [].The physical barrier includes a cellular component consisting of the vascular endothelium, the epithelial cell lining, and the mucus layer.A third aim was to determine whether fiber levels need to be standardized in a test for gut permeability by comparing measurements of permeability on standard diets containing 16.25 g or 32.5 g fiber/d. . These are addressed in the Supplementary Materials. 13, 14 Endpoints to evaluate intestinal permeability were urine excretion of probe .
The FD-4 intestinal permeability test was dose-dependent as we found a significant increase in plasma levels of FD-4 in obese mice with the bodyweight dose regimen. However, this difference was .
what causes increased intestinal permeability
Um telemóvel para videojogos de realidade aumentada. Um tablet que resiste às condições mais duras. O Android possibilita escolhas para tudo o que desejar. Saiba mais sobre o Android, a plataforma que mudou o que os dispositivos móveis podem fazer: de inovações úteis e segurança contínua à sincronização de todos os seus ecrãs.
urine test for intestinal permeability|what causes increased intestinal permeability